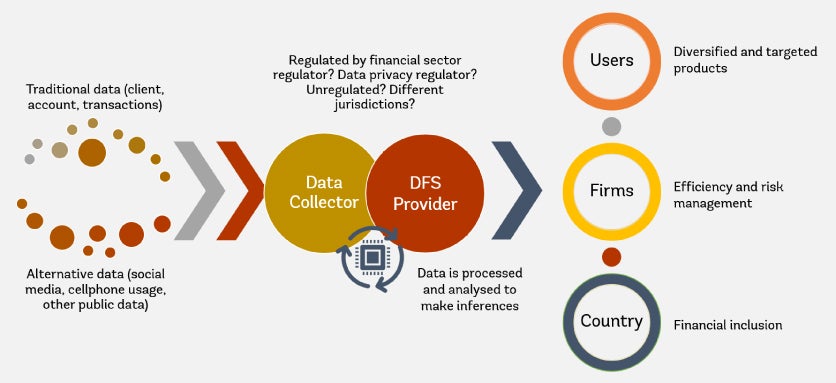
Potential Benefits of Data Privacy and Protection Frameworks for DFS
Large volumes of traditional and alternative forms of data is being collected, processed and used. This has accelerated development of the DFS landscape with potential benefits for users, firms, and countries.
Benefits
Wider choice in products and channels
- Credit products for those without formal credit histories.
- Customized savings and investment products.
- Real-time digital payments.
Customized products and services
- Personalized loan sizes, repayment schedules and pricing.
Easier and secure identification
- Electronic know-your-customer (e-KYC) processes through national ID systems.
- Strong customer authentication for transactions.
Effective targeting of government support programs
- Rapid and effective transfer of subsidies and cash transfers.
Faster information sharing and complaint handling
- Chatbots for information about products, services and frequently asked questions.
- Automated complaint lodging and resolutions.
Country-level increase in financial inclusion
- Aligning data privacy and protection reforms with financial inclusion strategies or broader DFS reforms.
Country Examples

Electronic KYC
In Kenya, mobile money operators can verify onboarded customers against the government database in real-time, creating efficiencies and assurances of data accuracy. Depositors in Kenya who use the M-Shwari mobile savings account can use their national IDs to verify their identities, in turn receiving higher balance limits on their savings accounts, as well as access to credit. (The first tier of Kenya’s KYC regulations allows mobile money customers to use their SIM cards to identify themselves.) Kenya has also built an Integrated Population Registration System (IPRS) to verify the identity of citizens and residents. Commercial banks, mobile money providers and other financial service providers are able to access this database to authenticate the identity of customers during the onboarding process.

Alternative Credit Scoring
Micro, small and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) often encounter difficulties when accessing finance for their business growth and operations. Compared with large corporations, MSMEs may not have sufficient credit history and readily available financial records. WeLab developed tech-enabled credit platforms which collect, use and process alternative data using artificial intelligence and big data analytics. For credit scoring of MSMEs in China, two types of alternative data are typically obtained.
Merchant business data: Fintech lenders usually work with two major types of loan sourcing channels (or thirdparty data providers) to assess the creditworthiness of MSMEs, namely E-marketplaces and Point-of-Sale service providers. Depending on their partnership agreement, these channels can provide data about merchant profiles, merchant popularity, refund histories, and sales data on the transaction level or on a summarised level. To protect the interests of the channel and the privacy of its merchant customers, in most cases, the fintech lender will engage the channel to develop a pre-screening model that performs credit scoring based on the data of the channel’s MSME clients. The credit scoring is carried out by the channel on-site so that no confidential data is leaked. MSMEs with favourable credit scoring outcomes are labelled as whitelisted merchants by the channel. This pre-screening model not only reduces credit risk but also increases the approval rate, thus enhancing the customer experience by offering loan promotions/ options only to whitelisted merchants from the channel.
Personal credit history of the business owner: Some data vendors can provide the credit history of business owners, gathered from non-bank FIs. Information provided may include delinquencies, number of loan enquiries and/or number of existing loans, fraud blacklists, and details of individuals who have defaulted. Some large vendors can also provide an alternative credit score for business owners, developed on the basis of demographic data and spending behaviour.

Open Banking
Hong Kong recognized the importance of data availability and data sharing infrastructures, particularly in the context of DFS providers using alternative data.
In 2018, the HKMA formulated the Open Application Programming Interface (API) Framework to facilitate data exchange between banks and third-party service providers (TSPs). HKMA is exploring a new data strategy and will consider building a new financial infrastructure, namely Commercial Data Interchange (or ’CDI’). CDI is a consent-based infrastructure that enables more direct, secure and efficient data flow between banks and sources of commercial data to enhance inclusive finance in Hong Kong. With CDI, we anticipate that enhanced financial products and services could be offered to MSMEs which are in full control of their own digital footprint.

Targeting Government Support Programs
When COVID-19 hit and quarantines began, the Philippines was one of about 20 countries in the world without a national ID system. It needed a massive expansion of social protection coverage to mitigate the impacts of the pandemic. Countries that already had good and inclusive digital infrastructure (including internet connectivity, digital identification, digital payments and integrated data ecosystems) were better equipped to quickly adapt their social protection programs to meet urgent needs.
By 2022, the Philippine Statistics Authority (PSA) implemented the Philippine Identification System (PhilSys) project, and also launched PhilSys Check, an authentication system for the Philippine Identification (PhilID) card.
The Department of Social Welfare and Development (DSWD) has adopted PhilSys for the Philippines’ social protection and digital transformation journeys. DSWD was the first agency to utilize the secure biometric and SMS-based identity authentication offered by the PhilSys to uniquely identify and verify its beneficiaries.
Those who interact with the DSWD will face less paperwork, queues, hassle, costs and time. With their PhilSys ID, they will also have better access to a bank or e-money account where they can potentially receive payments directly in the future, promoting financial inclusion. Indeed, more than 5 million low-income Filipinos have already opened bank accounts during PhilSys registration. And the resources that DSWD saves can be redirected to addressing the needs of beneficiaries who live in remote areas without easy access to internet and social protection programs.

Account Aggregators
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) created account aggregators (AAs) in 2018 to simplify the consent process for customers. In most open banking regimes, financial information providers (FIPs) and financial information users (FIUs) directly exchange data. This direct model of data exchange—such as between a bank and a credit bureau—offers customers limited control and visibility into what data are being shared and to what end. AAs have been designed to sit between FIPs and FIUs to facilitate data exchange more transparently. Despite their name, AAs are barred from seeing, storing, analyzing, or using customer data. As trusted, impartial intermediaries, they simply manage consent and serve as the pipes through which data flow among FSPs. When a customer gives consent to a provider via the AA, the AA fetches the relevant information from the customer’s financial accounts and sends it via secure channels to the requesting institution.
Other countries that are looking to implement similar systems or systems to perform similar functions should examine the types of institutions and regulatory frameworks already in place. In addition, countries should examine their institutional capacity to implement, regulate, and supervise an open banking system and the potential demand for sharing financial information digitally.
Key Concerns for DFS Users
Understanding data privacy concerns from the perspective of a DFS user is a critical first step towards policy and regulatory reforms which balance rights of users and obligations of providers.
Emerging Risks and Mitigants
Data privacy risks are evolving rapidly with varying mitigating actions being tested in different markets.
Guiding Principles
The guiding principles are intended to support a risk-based proportionate regulatory framework for data privacy and protection in a DFS context.
Implementation
There are three ways that the guiding principles could be implemented. They include
- an overarching law on data protection and privacy.
- incorporating data protection aspects in existing and related financial sector regulations.
- code of practice developed by industry association or representative body.
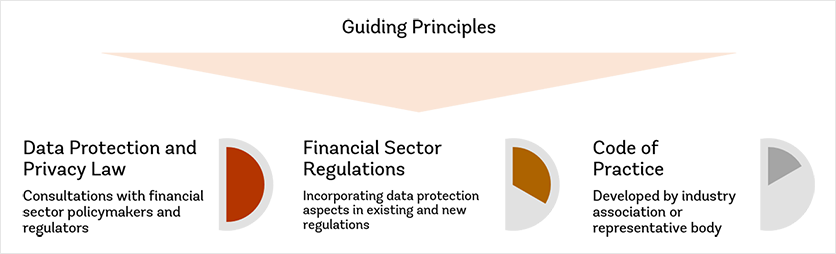
These approaches are not mutually exclusive and may be used to complement each other and provide a comprehensive framework.
In all cases, financial sector policymakers and regulators could consider a set of minimal actions (such as market risk assessments and stakeholder awareness) in the interim period before an implementation approach is finalized.
The extent to which the guiding principles are relevant for a country will depend on various factors. These include identified benefits and risks, policy priorities, existing legal and regulatory frameworks, supervisory and enforcement capacity, and market dynamics.
Overall, there should be effective consultation to identify the scope and coverage of laws, regulations, and guidelines. The guiding principles may provide the basis for consultation.